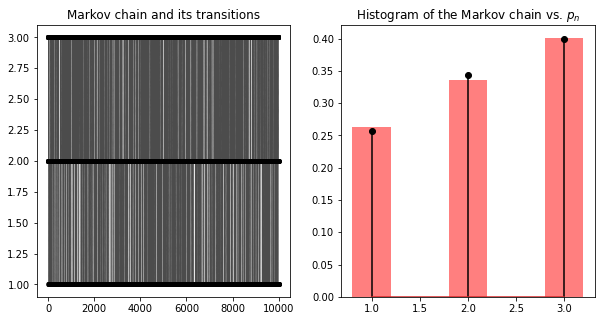
Example 5.1#
Simulating a Markov chain with a given transition matrix.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
rng = np.random.default_rng(42)
def discrete(s, w):
cw = np.cumsum(w)
u = rng.uniform(0, 1)
for i in range(len(cw)):
if cw[i] >= u:
return s[i]
M = [[0.6, 0.2, 0.2], [0.3, 0.5, 0.2], [0, 0.3, 0.7]]
def sample_Markov_chain(s, M, s_curr):
return discrete(s, M[s_curr])
s = [0, 1, 2]
N = 10000
seq = np.zeros(N, dtype=int)
seq[0] = 0
p = np.zeros((3, N))
p[:, 0] = [1, 0, 0]
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))
for n in range(1, N):
seq[n] = sample_Markov_chain(s, M, seq[n - 1])
p[:, n] = p[:, n - 1] @ M
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(seq[:N-1] + 1, 'ko--', markersize=4, linewidth=0.2, alpha=0.7)
plt.title('Markov chain and its transitions')
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.hist(seq[:N-1] + 1, bins=[1, 2, 3, 4], density=True, rwidth=0.4, color='r', alpha=0.5, align='left')
plt.stem([1, 2, 3], p[:, N-1], markerfmt='o', linefmt='k-')
plt.title('Histogram of the Markov chain vs. $p_n$')
plt.show()