Metropolis-Hastings algorithm#
As we have seen in the slides, for a generic target \(\pi(x) \propto \gamma(x)\) and a proposal \(q(x' | x)\), the Metropolis-Hastings algorithm is defined as follows. Given the state of chain \(x_{n-1}\), one iteration of this method goes as follows:
Sample \(x'\) from \(q(x' | x_{n-1})\)
Compute the acceptance probability \(\alpha(x_{n-1}, x') = \min\left(1, \frac{\pi(x') q(x_{n-1} | x')}{\pi(x_{n-1}) q(x' | x_{n-1})}\right)\)
Sample \(u \sim \mathcal{U}(0, 1)\)
If \(u < \alpha(x_{n-1}, x')\), set \(x_n = x'\), otherwise set \(x_n = x_{n-1}\)
Repeat
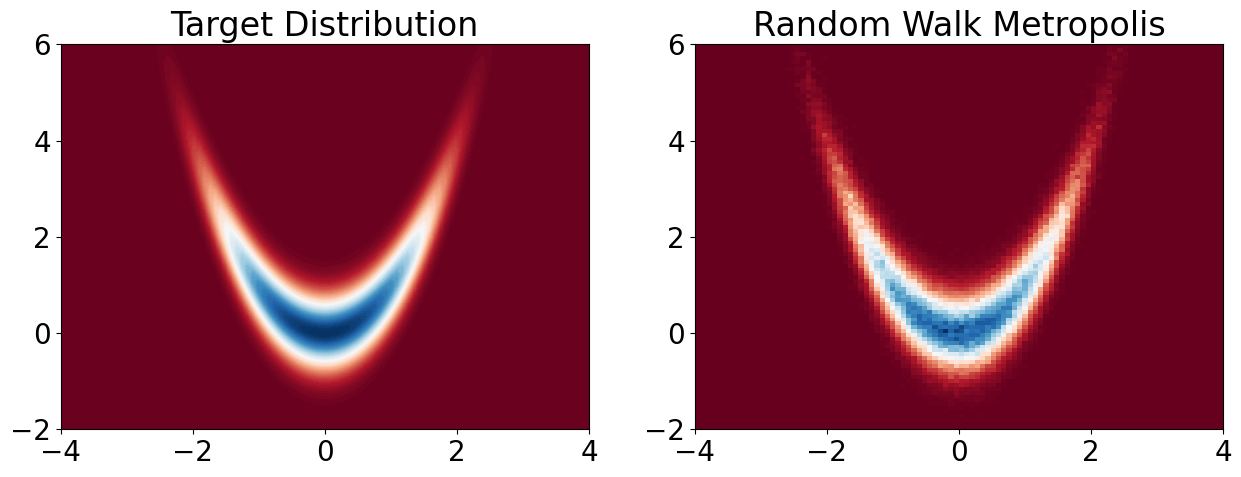
Let us try this on the Banana density example. Recall that this density is defined on \(\mathbb{R}^2\) and is given by
In this case, we have the unnormalised density
We will now choose our proposal as the random walk proposal
where \(\sigma_q^2\) is a parameter that we can tune. We will also choose the initial state of the chain to be \(x_0 = (0, 0)\).
Note that, since \(q(x' | x) = q(x | x')\), the acceptance probability simplifies to
The following code implements the Metropolis-Hastings algorithm for the Banana density.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
rng = np.random.default_rng(24)
# banana function for testing MCMC
def log_gamma(x):
return -x[0]**2/10 - x[1]**2/10 - 2 * (x[1] - x[0]**2)**2
N = 1000000
samples_RW = np.zeros((2, N))
# initial values
x_1 = 0
x_2 = 0
samples_RW[:, 0] = np.array([x_1, x_2])
# parameters
gamma = 0.005
sigma_rw = 0.5
burnin = 200
for n in range(1, N):
# random walk
x_s = samples_RW[:, n-1] + sigma_rw * np.random.randn(2)
# metropolis
u = rng.uniform(0, 1)
if np.log(u) < log_gamma(x_s) - log_gamma(samples_RW[:, n-1]):
samples_RW[:, n] = x_s
else:
samples_RW[:, n] = samples_RW[:, n-1]
# for surf plot banana 2d
x_bb = np.linspace(-4, 4, 100)
y_bb = np.linspace(-2, 6, 100)
X_bb, Y_bb = np.meshgrid(x_bb, y_bb)
Z_bb = np.exp(log_gamma([X_bb, Y_bb]))
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 5))
# make fonts bigger
plt.rcParams.update({'font.size': 20})
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
cnt = plt.contourf(X_bb, Y_bb, Z_bb, 100, cmap='RdBu')
plt.title('Target Distribution')
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.hist2d(samples_RW[0, burnin:n], samples_RW[1, burnin:n], 100, cmap='RdBu', range=[[-4, 4], [-2, 6]], density=True)
# remove the white edges from plt.hist2d
plt.title('Random Walk Metropolis')
plt.show()